By Julliane Silveira, scientific journalist, São José dos Campos, SP, Brazil
Welding is one of the main techniques used for manufacturing, maintenance and recovery of metallic pieces and products. It is a technique that may be influenced by industrial modernization. The industry around the world is changing and adopting faster and more economical procedures to increase productivity and reduce the environmental impact of production processes.
Another important trend on the shop floor is the integration of processes and the development of “smarter” factories. In this context, laser technology is essential and has been singled out as one of the main ones, which fully meet the requirements of the industry 4.0 concept.
At the same time, laser materials processing has received special attention from the automotive and aerospace industries in recent years, which greatly contributes to the encouragement of research and development of new technologies (STEEN; MAZUMDER, 2010).
For this reason, the study of laser welding techniques is fundamental for the development of processes that meet the needs of the most modern production.
It is the subject of the article “A Comparative Study of the Heat Input During Laser Welding of Aeronautical Aluminum Alloy AA6013-T4”, published in the current issue of JATM (Journal of Aerospace Technology and Management). The effect of two different heat inputs in laser beam welding of a high strength aluminum alloy AA6013-T4 was evaluated from macrostructural and microstructural points of view. The heat input is the amount of energy supplied per unit length of the welded workpiece. It is also known as welding energy.
High-strength aluminum alloys, like the AA6013, have been gaining space and reliability mainly in the aerospace industry, in the joining of the stringers to the fuselage (MENDEZ; EAGAR, 2001). Their characteristics and metallurgical properties allow great advantages and a high quality in their laser process (LEIGH, et al., 2002). “We chose this aluminum alloy due to its importance in aircraft construction and presents challenges for welding, such as defects like pores and cracks, entanglements and distortions, which should be reduced with the application of laser technology,” explains Milton de Lima, study leader and researcher at the Department of Aerospace Science and Technology at the Brazilian Institute of Advanced Studies (IEAv).
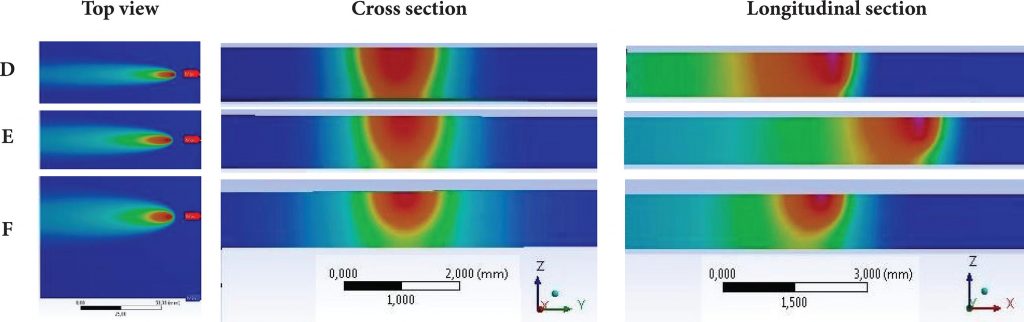
Figure 1. Thermal gradient simulation (top view, cross section, longitudinal section) for samples (D), (E), and (F).
According to Lima, the heat input is one of the most important parameters to be optimized in routine industrial welding processes. However, the study showed that welding energy is not the most important factor for laser welding, although it is considered a very important parameter for metallurgy.
With the advance of new technologies in the “smart” industry and the widespread use of laser, professionals need to seek new parameters to ensure production excellence. “The conclusion of our article is that the welding practice must be modified to meet the most modern technologies needs. From now on we will see laser welding in the industry and we will need specialized technicians and managers”, adds Lima.
The results indicate that the heat input is not a convenient method to parameterize the laser beam welding parameters aiming the same weld features.
References
LEIGH, B.R., et al. An evaluation of the physical properties of Nd: YAG laser welded high strength 6000 series aluminum alloys. In: ICAS 2002 Congress, Toronto, 2002.
MENDEZ, P.F. and EAGAR, T.W. Welding processes for aeronautics. Advanced Materials & Processes. 2001, vol. 159, no. 5, pp. 39-43, ISSN: 0882-7958 [viewed 05 November 2018]. Available from: https://dmse.mit.edu/publications/welding-processes-aeronautics
STEEN, W.M. and MAZUMDER, J. Laser material processing. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-84996-062-5. London: Springer-Verlag, 2010.
To read the article, access it
COELHO, B.N., et al. A Comparative Study of the Heat Input During Laser Welding of Aeronautical Aluminum Alloy AA6013-T4. J. Aerosp. Technol. Manag. [online]. 2018, vol.10, e2918, ISSN: 1984-9648 [viewed 05 November 2018]. DOI: 10.5028/jatm.v10.925. Available from: http://ref.scielo.org/n8jwpj
External link
Journal of Aerospace Technology and Management – JATM: <http://www.scielo.br/jatm>
Como citar este post [ISO 690/2010]:
















Recent Comments