Since 2010, two biological products have been developed by the CEVAP/UNESP, the fibrin sealant and the apilic antivenom. In 2022, UNESP has begun the construction of a Factory for the Production of Pilot Batches for Clinical Research. This pioneering initiative will contribute to the establishment of biopharma innovation ecosystems and creation of wealth in the country. … Read More →
Isolation and characterization of new compounds derived from animal poisons and venoms: challenges and perspectives
The Laboratory of Animal Toxins is equipped to perform the isolation, biochemical, structural and functional characterization of toxins from animal venoms, as well as the heterologous expression of molecules with potential biotechnological application. PEGylation of peptides and proteins is also carried out to increase their potential use as a drug. … Read More →
New standard operating procedure for apitoxin collection aiming at research and production of the apilic antivenom
A new apilic antivenom was developed to reduce the mortality of patients envenomed by Africanized honeybees. This species has an intensely defensive behavior and promotes several fatal accidents. In the process of collecting apitoxin it is essential to guarantee the safety of the handler, the welfare of bee colonies and the quality of biomolecules. … Read More →
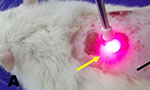
Laser therapy together with a fibrin biopolymer improves nerve and bone tissue regeneration
The heterologous fibrin sealant produced by CEVAP has been employed as “nerve glue” and wound healing substance for venous ulcers. Currently it is called fibrin biopolymer due to its multiple uses. In association with adjuvant scaffolds, it constitutes active biocomplexes that contribute to the morphophysiological and functional recovery of bone defects. … Read More →
Building an electronic scientific journal: evolution and challenges
Twenty-eight years ago, the Journal of Venomous Animals and Toxins including Tropical Diseases was launched with ambitious goals: to be an e-journal even before internet was accessible to the general public and to establish itself as an international publication born in Brazil. Since then, many obstacles and challenges have been and continue to be overcome. … Read More →
Tools of death with a touch of romance: all the amazing things scorpions use their weapons for
In the world of animal weaponry, scorpions stand out by having two separate weapons, used in many different ways. The authors consolidate 150 years of research in the perspectives of feeding, defense and sexually related contests. An exciting guided tour into scorpion weapon biology and a reference for researchers. … Read More →
β-scoliidine, present in Japanese solitary wasp venom, protects neuronal cells from oxidative stress
Solitary wasp venoms represent a rich source of molecules of pharmacological interest. Thus, to unravel the content of Scolia decorata ventralis venom, proteomic techniques were used, and two new peptides were determined as its major components, α-scoliidine and β-scoliidine. Interestingly, β-scoliidin was effective in protecting neuronal cells against oxidative stress. … Read More →
Spider venom neurotoxins from the Philippine tarantula: a new source for biomedical leads
When the words “venom” and “spider” are mentioned, most people shiver with fear and will go to any extent to avoid them. However, this is not the case with spider venom researchers in the Philippines as they explore the novel neuroactivities of the venom of this endemic, medium-sized theraphosid, Phlogiellus bundokalbo. … Read More →
Chondroitin Polymerizing Factor and its therapeutic function for the clinical treatment of lung cancer
Lung cancer is the most common malignancy worldwide and is characterized by rapid progression, aggressive behavior, frequent recurrence, and poor prognosis. Study investigate the function of CHPF in lung cancer, lentiviral vectors expressing CHPF shRNA were stably transduced into A549 and H1299 cells. Compared to shCtrl cells, CHPF knockdown cells had significantly reduced proliferation. … Read More →
Coronavirus Sars-Cov-2 responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic is a specialist in infecting humans
ACE2 is the protein used by new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) to enter the host-cells. Our comparative analysis with 70 mammals revealed a relatively high diversity of ACE2 between these species, but no polymorphism within human populations, at least considering 30 sites located at the ACE2 binding sites to the SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 can infect any human from any population, but it is unable to infect, naturally and easily, other mammals, including pets. … Read More →


















Recent Comments