The study discusses Anísio Teixeira’s analysis about the importance of the democratic, public, universal, free, mandatory, and efficient school as a citizen’s right and duty of the State Government. This concept of school and an emancipatory education are conditions for human development and social integration. … Read More →
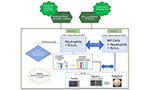
Snake venom toxin activates immune cells and decreases the invasion potential of tumor cells
BJcuL toxin – isolated from the venom of the Brazilian snake Bothrops jararacussu – was able to stimulate cells of the immune system to act against tumor cells. Blood neutrophils, when stimulated by BJcuL, reduced the migratory potential of neuroblastoma cells in culture. … Read More →
Study analyzes the presence of bacteria in vacuum-packed meat
Meat that is out of date has changes in color, strong odor and production of limosity. These characteristics are due to the combination of biological and chemical events caused by the presence of deteriorating bacteria. This study analyzed the behavior of bacteria where they estimated the shelf-life of vacuum-packed beef and stored under cooling. … Read More →
How China grew economically and still created the world’s largest higher education system
China experienced significant economic growth and built the largest higher education system in the world. What is the relationship between these factors? To answer this question, the research aimed to understand the role of the economy and Projects 211 and 985 for the expansion of Chinese higher education. … Read More →
Occupational risk: COVID-19 infection among health workers is greater in general wards than in intensive care units
The study highlights in what extent scarcity of personal protective equipment (PPE), inadequate use and non-usage of tPPE, and work overload constitute reasons for COVID-19 infection among health care teams. In addition, the investigation determined how work overload in health care system may increase the number of deaths associated with COVID-19 among health workers. … Read More →
Can music contribute to the cognitive health of the elderly?
The aging of the population is a worldwide phenomenon. It is urgent to develop strategies to prevent or delay cognitive decline. The study presents the results of a research that sought to know the effects of musical activities on the elderly, indicating that music can contribute to cognitive health. … Read More →
Macrofauna as an Alternative for Soil Recovery
Macrofauna is essential for the soil food chain and its analysis is efficient to indicate environmental quality. The research evaluated the macrofauna of the soil of an area under recovery and with different types of vegetation cover and the results showed two plant species as an alternative for the recovery of degraded soils in the Brazilian Cerrado. … Read More →
Evaluating alcohol use and adherence to an online intervention among college students
The use of the internet has facilitated the provision of health strategies. Despite favoring access to many people, adherence to the interventions is relatively low. This study evaluated factors associated with adherence to an online brief intervention on alcohol use among university students. … Read More →
The impact of unemployment and psychological well-being
This study aimed to analyze the moderating power of unemployment time in the relationship between the value of work and psychological well-being. The results demonstrate that the time of unemployment associated with the intrinsic values of work can increase the experience of well-being and stabilize the negative affects caused by unemployment. … Read More →
Aircraft development under the Mass Properties Management perspective
Aircraft mass properties, such as weight, are established during aircraft conception. Those properties usually are subject to deviations during aircraft development, which leads to a reduction of the desired performance and rework in the development process. This study presents a proposal to reduce rework, keeping the planned performance, and resulting in higher project efficiency. … Read More →





















Recent Comments