Food products and goods, such as corn kernels, may eventually be contaminated by fungi. In recent research, ginger essential oil was analyzed as a possible alternative to be a synthetic fungicides, by inhibiting the development of fungi in corn kernels. The results showed antifungal efficacy of the essential oil of ginger against the fungus Aspergillus flavus. … Read More →
Transport of cattle influences meat quality
Quality meat is the result of several factors such as food, production and also the transport of cattle. For greater economic profitability, transport with a high rate of stocking of the bodies is common, but it results in hematomas in the bovine carcasses. Study analyzed three types of bodies, their stocking rate and the incidence of hematomas in the carcasses of cattle. … Read More →
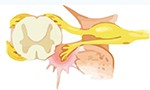
How can the use of a biological glue allow motor recovery after spinal cord injury?
Upper and lower limb injuries are common outcomes of accidents. There is no significant recovery and surgical options are quite limited. A research has developed a new therapy by using the fibrina sealant produced by the Center for the Study of Venoms and Venomous Animals (CEVAP) conjugated with the drug dimethyl fumarate. The results are encouraging regarding mobility recovery. … Read More →
Face masks: how important are they in a pandemic?
The use of homemade fabric face mask constitutes an important non-pharmacological intervention to protect population against infection by bacteria and viruses, especially in a pandemic situation. This intervention combined with hygiene, disinfection of high-touch surfaces, and cough etiquettes are efficient measures to prevent transmission of coronavirus. … Read More →
Mental health of the general population and health professionals during the COVID-19 pandemic
Aside from concerns regarding physical health, COVID-19 entails repercussions in mental health as well. The population in general and health professionals in particular have reported symptoms of depression, anxiety and stress. Rapid changes in routine and financial instability may also affect interpersonal relationships and psychological well-being. … Read More →
Chondroitin Polymerizing Factor and its therapeutic function for the clinical treatment of lung cancer
Lung cancer is the most common malignancy worldwide and is characterized by rapid progression, aggressive behavior, frequent recurrence, and poor prognosis. Study investigate the function of CHPF in lung cancer, lentiviral vectors expressing CHPF shRNA were stably transduced into A549 and H1299 cells. Compared to shCtrl cells, CHPF knockdown cells had significantly reduced proliferation. … Read More →
Health professionals fighting COVID-19 in hospitals and risking their health and life to care of infected patients
The paper discusses the challenge faced by health professionals delivering care to patients with COVID-19, and who are at high risk for infection. The adequate use of personal protective equipment reduces the risk, however, there is a need to have adequate provision of these protective materials available, and also trained professionals who can use them. … Read More →
Organic agriculture brings quality of life to producers
Organic agriculture’s main characteristic is the production of food and other products without the use of chemicals. The use of these products, such as pesticides and pesticides, are harmful not only to consumers, but also to those who produce these foods. In search of evidence that shows the quality of life of organic farmers, a review gathered eleven papers on this theme. … Read More →
Mozambican women in science – a challenge and a story to be told
A network of knowledge circulation and exchange of experiences has been consolidated over the last few years between Brazilian and Mozambican academic feminists. We highlight a topic still little known in Brazil – women in science in Mozambique – interviewing three researchers who tell a little about this story. … Read More →
Coronavirus Sars-Cov-2 responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic is a specialist in infecting humans
ACE2 is the protein used by new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) to enter the host-cells. Our comparative analysis with 70 mammals revealed a relatively high diversity of ACE2 between these species, but no polymorphism within human populations, at least considering 30 sites located at the ACE2 binding sites to the SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 can infect any human from any population, but it is unable to infect, naturally and easily, other mammals, including pets. … Read More →


















Recent Comments